Web Page: Start Budgeting
Web Pages: How Car Insurance Works
Web Page: How Health Insurance Works
Web Pages: How Homeowners Insurance Works
Web Pages: How Liability Insurance Works
Web Pages: How Life Insurance Works
Money management includes all the activities you’ve learned about so far—earning, saving, purchasing, borrowing, and investing. Successful money management creates a smooth and consistent cash flow rather than a cycle of feast or famine. The tool that brings all of these factors together is a budget.
A budget is a plan for balancing income and expenses. It is also a tool for assessing how well you are doing so that you can make adjustments. Some income and expenses are fixed—the amount you are always paid and the amount you always pay out. Other income and expenses vary. In the example budget below, the budget amounts were filled in before the month of June as a prediction, and the actual amounts were filled in afterward.
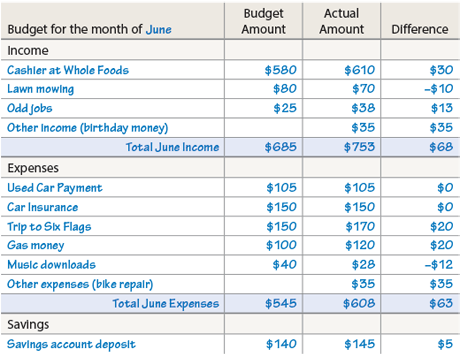
Your Turn Go to thoughtfullearning.com/h308 to download a budget template. Considering your own situation, fill in the first two columns for next month. Include both fixed and variable income and expenses. At the end of the month, fill in the last two columns of the budget. Were your predictions correct? Explain.
As you have learned about investing, part of managing money is managing risk. Low-risk investments tend to have low-yield returns, while high-risk investments can have high-yield returns—or losses. Unexpected life events present another kind of risk.
The first defense against emergencies is to set up a savings account (see page 296). By putting aside a certain amount of money each paycheck, you’ll eventually have the recommended three to six months of income stored up to support you.
However, some emergencies may require a great deal of money or may limit your earning ability. To prepare for such events, you need to have insurance.
Insurance comes in various forms to help you manage risk in different areas of your life. Each insurance policy document outlines the terms of that particular policy, the premiums you must pay, and the benefits the insurance company will pay you under specific circumstances. Contact a professional insurance agent before you make any insurance decisions. Here are the basic types of insurance:
You, your employer, or both pay the premium that purchases an insurance policy. In addition, you may be required to make co-payments for services as well as pay a percentage of costs not fully covered by your policy.
Your Turn Which types of insurance do you currently have? Which type would you like to have? Investigate options for purchasing that type of insurance. What would the premiums be? What benefits would you receive?
Web Page: Start Budgeting
Web Pages: How Car Insurance Works
Web Page: How Health Insurance Works
Web Pages: How Homeowners Insurance Works
Web Pages: How Liability Insurance Works
Web Pages: How Life Insurance Works
© 2014 Thoughtful Learning
